As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases
Lewy Body Dementia in the UK is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that causes cognitive and motor impairments. Lewy Body Dementia is a type of dementia that affects individuals in the UK.
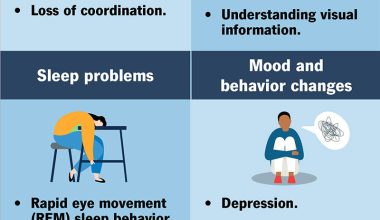
It is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that leads to a decline in cognitive abilities and motor skills. The disease is characterized by the presence of abnormal protein deposits, called Lewy bodies, in the brain. These deposits interfere with the normal functioning of brain cells, leading to symptoms such as memory loss, confusion, hallucinations, and problems with movement and balance.
Lewy Body Dementia can be challenging to diagnose and manage, as it shares similarities with other neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. However, with proper care and support, individuals with Lewy Body Dementia can maintain their quality of life for as long as possible.

Credit: www.dementiauk.org
The Impact Of Lewy Body Dementia In The Uk
Lewy Body Dementia is a progressive neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. In the United Kingdom, this debilitating condition has a significant impact on individuals and their families. From prevalence and demographics to the challenges faced by patients and caregivers, understanding the impact of Lewy Body Dementia is crucial.
Prevalence And Demographics
In the UK, Lewy Body Dementia is the second most common form of progressive dementia after Alzheimer’s disease. It is estimated that around 100,000 people are living with this condition in the country today(Source: Alzheimer’s Society UK).
While the condition can affect people of all ages, it primarily affects individuals over the age of 65(Source: NHS UK).
Challenges Faced By Patients And Caregivers
Living with Lewy Body Dementia poses various challenges for both patients and their caregivers. The unpredictable nature of the symptoms, such as fluctuations in cognitive functioning and motor skills, can make daily life incredibly challenging.
For patients, these challenges can include difficulty with memory, confusion, visual hallucinations, and problems with movement and balance(Source: Lewy Body Society).
But it’s not just the patients who face difficulties; caregivers also bear a significant burden. They often have to navigate the complex healthcare system, manage medications, handle behavioral changes, and cope with their own emotional and physical strain while providing round-the-clock care.
The impact of the disease on caregivers is undeniable and can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and even depression(Source: Dementia UK).
To make matters more challenging, the lack of awareness and understanding surrounding Lewy Body Dementia can often lead to misdiagnosis and inadequate support from healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
Lewy Body Dementia is a condition that not only affects the individuals living with it but also has a profound impact on their families and caregivers. By understanding the prevalence, demographics, and challenges associated with this condition, we can provide better support and care for those affected by Lewy Body Dementia in the UK.
Diagnosis And Treatment Options
When it comes to Lewy Body Dementia (LBD), early detection and assessment are crucial for effective management and care. Timely diagnosis not only helps in understanding the progression of the disease but also enables healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans according to the individual’s needs.
Early Detection And Assessment
Early detection of Lewy Body Dementia can be challenging due to its overlapping symptoms with other neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. However, various assessment tools and evaluations can aid in a more accurate diagnosis. These assessments may include:
- Cognitive tests to assess memory, thinking, and problem-solving abilities
- Neurological examinations to evaluate movement, balance, and reflexes
- Psychiatric evaluations to identify changes in mood, behavior, and hallucinations
- Brain imaging scans, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or positron emission tomography (PET), to visualize abnormalities in brain structure or function
By combining the results of these assessments, healthcare professionals can determine the presence of Lewy bodies, abnormal proteins that accumulate in the brain, helping confirm the diagnosis.
Pharmacological And Non-pharmacological Interventions
Lewy Body Dementia treatment focuses on managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and supporting individuals and their families. Here are some treatment options that healthcare professionals may consider:
Pharmacological Interventions
Pharmacological interventions involve the use of medications to alleviate specific symptoms associated with Lewy Body Dementia. Although no cure exists for LBD, these medications can help manage cognitive decline, movement issues, and other related symptoms. Some commonly prescribed medications may include:
- Cholinesterase inhibitors like Donepezil (Aricept) to improve memory and thinking abilities
- Antipsychotic medications such as Quetiapine (Seroquel) or Clozapine (Clozaril) to address hallucinations and delusions
- Parkinson’s disease medications like Levodopa to relieve motor symptoms like stiffness, tremors, and slowness of movement
It is important for healthcare professionals to carefully monitor the use of these medications, as some can worsen certain LBD symptoms or interact with other medications.
Non-Pharmacological Interventions
Non-pharmacological interventions focus on enhancing the overall well-being and functioning of individuals with Lewy Body Dementia. These interventions can include:
- Physical therapy to improve mobility, balance, and strength
- Occupational therapy to assist with daily tasks and maintain independence
- Speech therapy to address speech and swallowing difficulties
- Supportive counseling and psychotherapy to manage emotional and psychological challenges
- Behavioral interventions and environmental modifications to minimize agitation, confusion, and falls
Non-pharmacological interventions play a crucial role in improving quality of life, reducing caregiver burden, and promoting independence for individuals living with LBD.
Support And Resources For Patients And Caregivers
Access To Specialized Care Services
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) can pose unique challenges for patients and their caregivers, requiring specialized care services to effectively manage the condition. In the UK, patients and caregivers have access to a range of specialized care services tailored to the specific needs of those affected by LBD. These services often include comprehensive assessment and management by multidisciplinary teams, neurology and geriatric medicine expertise, and access to clinical trials and research studies.
Community Support And Advocacy Groups
Community support and advocacy groups play a vital role in providing assistance and guidance to patients and caregivers dealing with Lewy Body Dementia in the UK. These groups offer a valuable network for sharing experiences, accessing practical advice, and receiving emotional support. Additionally, advocacy groups work tirelessly to raise awareness about LBD, drive research efforts, and influence policy changes to improve the quality of care and support available to those affected by the condition.
Care Planning And Management
In the care planning and management of Lewy Body Dementia in the UK, it is essential to consider the unique challenges and needs of individuals living with this progressive condition. Caregivers, healthcare professionals, and loved ones play a crucial role in providing support, creating a dementia-friendly environment, and managing symptoms and behaviors to enhance the quality of life for those affected. This section will explore these aspects in detail.
Creating A Dementia-friendly Environment
Creating a dementia-friendly environment is key to promoting comfort, independence, and overall well-being for individuals with Lewy Body Dementia. Consider the following strategies:
- Ensure a clear and clutter-free space to reduce confusion and improve mobility.
- Use contrast and color cues to improve visibility, such as brightly colored signs and labels on important objects.
- Organize furniture in a way that supports mobility and safety.
- Install handrails and grab bars in essential areas, such as bathrooms or staircases.
- Use simple and familiar items for daily activities, like simplified utensils or large-print calendars.
By implementing these changes, caregivers can create an environment that reduces frustration and supports autonomy, enabling individuals with Lewy Body Dementia to navigate their surroundings more comfortably.
Managing Symptoms And Behaviors
Managing symptoms and behaviors associated with Lewy Body Dementia is crucial to maintaining the individual’s quality of life. Below are effective approaches:
- Medication Management: Ensure medications are taken consistently and as prescribed to manage cognitive, motor, and psychiatric symptoms. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals is essential to adjust medications as necessary.
- Sleep Management: Establish a regular sleep routine and create a relaxing environment to improve sleep quality. Reducing caffeine intake, encouraging physical activity, and minimizing daytime napping can also help manage sleep disturbances.
- Behavioral Interventions: Engage in activities that promote mental and physical stimulation, as well as emotional well-being. Art therapy, music therapy, and reminiscence activities can provide positive experiences and help manage behavioral symptoms.
Moreover, proper communication techniques and developing an understanding of the person’s individual preferences and triggers can significantly assist in managing symptoms and behaviors associated with Lewy Body Dementia.
Research And Future Perspectives
The research on Lewy body dementia in the UK explores potential treatments and diagnostic advancements. Future perspectives aim to enhance understanding and support for patients and caregivers, with a focus on improving quality of life and promoting early detection of the disease.
When it comes to Lewy Body Dementia, ongoing research is crucial in order to better understand the disease, improve diagnosis methods, and develop more effective treatments. The future prospects for Lewy Body Dementia are promising, with advancements in research paving the way for innovative approaches to treatment and care.
Advancements In Dementia Research
Researchers and scientists are tirelessly working to unravel the complexities of Lewy Body Dementia. Their efforts have led to significant advancements in dementia research, bringing us closer to a better understanding of the disease. Some key areas of progress include:
- Genetic Discoveries: Through extensive genetic studies, researchers have identified specific genes linked to Lewy Body Dementia. These discoveries not only help in early detection but also shed light on the underlying mechanisms at play.
- Biomarkers: Biomarkers play a crucial role in identifying and monitoring the progression of Lewy Body Dementia. Groundbreaking research has identified potential biomarkers, such as changes in cerebrospinal fluid and specific proteins, that show promise in improving diagnostic accuracy.
- Brain Imaging: Innovative brain imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), have provided valuable insights into the structural and functional changes occurring in the brains of individuals with Lewy Body Dementia. These imaging tools aid in accurate diagnosis and tracking disease progression.
- Drug Development: Researchers are actively exploring potential therapeutic targets for Lewy Body Dementia. Emerging medications and therapies are undergoing clinical trials, offering hope for improved symptom management and slowing disease progression.
Innovative Approaches To Treatment And Care
Besides research advancements, there is a growing focus on innovative approaches to treatment and care for individuals with Lewy Body Dementia. These approaches aim to provide comprehensive support, enhance quality of life, and alleviate symptoms. Some notable approaches include:
- Person-Centered Care: The implementation of person-centered care, tailored to the individual’s unique needs and preferences, ensures a holistic approach to managing Lewy Body Dementia. It focuses on promoting autonomy, dignity, and preserving cognitive and physical functions.
- Multidisciplinary Teams: Collaborative efforts involving healthcare professionals, including neurologists, geriatricians, psychiatrists, nurses, and social workers, are crucial for providing comprehensive care to individuals with Lewy Body Dementia. These multidisciplinary teams work together to address the complex needs of patients and their families.
- Non-Pharmacological Interventions: Non-drug approaches, such as cognitive stimulation therapy, sensory-based interventions, and music therapy, have shown promise in improving cognitive functioning, reducing behavioral symptoms, and enhancing overall well-being.
- Support for Caregivers: Recognizing the importance of support for caregivers, various initiatives have been established to provide education, respite care, and emotional support. These resources help caregivers navigate the challenges of caring for someone with Lewy Body Dementia and prevent burnout.
The combined efforts of ongoing research and innovative approaches to treatment and care offer hope for a future where individuals with Lewy Body Dementia can lead fulfilling lives with enhanced support and improved outcomes.

Credit: www.factmr.com

Credit: www.globaldata.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Lewy Body Dementia Uk
What Are 3 Signs Of Lewy Body Dementia?
The three signs of Lewy body dementia include visual hallucinations, fluctuating cognitive abilities, and motor symptoms such as tremors or Parkinson’s-like movements.
What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Lewy Body Dementia?
The life expectancy of someone with Lewy body dementia varies, but it is generally around 5 to 7 years. This progressive neurodegenerative disorder causes cognitive decline, movement problems, and changes in behavior that impact life expectancy. Proper care and management can help improve quality of life.
At What Age Does Lewy Body Dementia Start?
Lewy body dementia can start around the age of 50, but it can also occur in older individuals. Early symptoms may be mild and often misdiagnosed. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider if you suspect any cognitive changes or symptoms related to dementia.
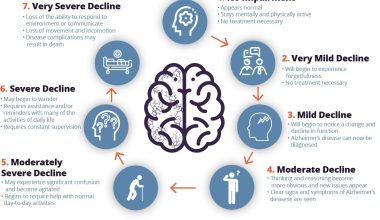
What Are The 7 Stages Of Lewy Body Dementia?
The 7 stages of Lewy body dementia are: mild cognitive impairment, early dementia/mild cognitive decline, moderate dementia, moderately severe dementia, severe dementia, and very severe dementia. Each stage presents different symptoms and challenges.
Conclusion
Lewy Body Dementia can have a profound impact on individuals and their families. Awareness and understanding are crucial for providing the best support and care. By staying informed about the symptoms, challenges, and available resources, we can create a more compassionate and supportive environment for those affected by this complex condition.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases