As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases
Lewy body dementia symptoms include cognitive decline, motor impairments, and hallucinations, among others. Lewy Body Dementia, also known as LBD, is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects the brain and causes a range of symptoms.
This condition is characterized by a buildup of abnormal protein deposits, called Lewy bodies, in the brain. The symptoms of LBD can vary from person to person but commonly include cognitive decline, motor impairments, and hallucinations. Cognitive decline may manifest as memory loss, confusion, and difficulty with problem-solving and planning.
Motor impairments often involve muscle stiffness, tremors, and slowed movements. Hallucinations, primarily visual, may also occur, along with fluctuations in alertness and attention. Other symptoms can include sleep disturbances, depression, and changes in autonomic functions, such as blood pressure regulation. Understanding the symptoms of Lewy body dementia is essential for early detection and effective management of the disease.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/difference-between-alzheimers-and-lewy-body-dementia-98749_final-8498478f530b4c499cd623b82ff806b7.jpg)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
What Is Lewy Body Dementia?
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) is a complex and challenging brain disorder that affects a person’s ability to think, move, sleep, and regulate their autonomic body functions. It is characterized by the presence of abnormal protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain, which disrupt the normal functioning of brain cells. LBD is the third most common cause of dementia after Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia, and it can be challenging to diagnose due to its overlapping symptoms with other neurodegenerative disorders.
Distinctive Brain Changes
LBD is distinguished by the presence of Lewy bodies in the cerebral cortex, particularly in the areas responsible for thinking, memory, and motor control. These abnormal protein aggregates disrupt the communication between nerve cells, leading to cognitive impairment and motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia. Additionally, LBD is associated with a loss of cholinergic neurons, further contributing to cognitive decline and behavioral changes.
Similarities To Other Dementias
While LBD shares some clinical features with other dementias, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, its distinct neuropathological characteristics set it apart. Patients with LBD may experience fluctuations in their cognition and attention, visual hallucinations, and REM sleep behavior disorder, distinguishing it from other forms of dementia. The overlap of symptoms with other neurodegenerative disorders can complicate the accurate diagnosis of LBD and require specialized assessments by healthcare providers experienced in neurodegenerative diseases.

Credit: www.njmemorycenter.com
Early Symptoms Of Lewy Body Dementia
Recognizing the early symptoms of Lewy Body Dementia is crucial for early detection and intervention. This progressive neurodegenerative disorder can affect various aspects of a person’s cognition, movement, and behavior. Understanding these early signs can help individuals and their loved ones seek medical assistance promptly, improving the overall management of the disease.
Cognitive Changes
Lewy Body Dementia typically begins with subtle cognitive changes, often resembling those seen in other forms of dementia such as Alzheimer’s disease. These changes may include:
- Memory loss, particularly short-term memory.
- Difficulty with attention and concentration.
- Problems with problem-solving and decision-making.
- Confusion and disorientation in familiar surroundings.
These cognitive symptoms can impact everyday tasks and may gradually worsen over time.
Visual Hallucinations
Visual hallucinations are a distinctive early symptom of Lewy Body Dementia. Individuals may experience vivid and often recurring hallucinations, seeing things that are not there. These hallucinations can range from simple shapes and colors to complex images and people. It’s important to note that individuals with Lewy Body Dementia are often aware that these hallucinations are not real, which can cause distress and anxiety.
The presence of visual hallucinations, especially when combined with other cognitive and movement-related symptoms, can suggest the possibility of Lewy Body Dementia.
Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism, characterized by motor symptoms similar to those seen in Parkinson’s disease, is another early sign of Lewy Body Dementia. These symptoms may include:
- Tremors or shaking, primarily at rest.
- Stiffness and rigidity in the muscles.
- Slowed movement and impaired coordination.
In some cases, individuals with Lewy Body Dementia may even experience these motor symptoms before cognitive changes become noticeable. This distinction can sometimes make it challenging to differentiate between Lewy Body Dementia and Parkinson’s disease.
Overall, recognizing the early symptoms of Lewy Body Dementia is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate care. If you or a loved one is experiencing any of these signs, it’s essential to consult a medical professional for further evaluation and guidance.
Advanced Symptoms Of Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) is a complex and progressive brain disorder that can present a wide range of symptoms. As the disease advances, certain symptoms become more pronounced, affecting various aspects of a person’s daily life. Understanding these advanced symptoms is crucial for caregivers and healthcare professionals to provide the necessary support and care. In this article, we will explore three significant advanced symptoms of Lewy Body Dementia: Fluctuating cognition, REM sleep behavior disorder, and autonomic dysfunction.
Fluctuating Cognition
One of the hallmark features of Lewy Body Dementia is the fluctuation in cognitive abilities. People with LBD may experience periods of clarity and alertness, followed by sudden declines in their cognitive functions. These fluctuations can occur throughout the day, making it challenging for individuals to maintain a consistent level of focus and attention.
This cognitive instability can manifest as memory problems, difficulty with problem-solving and decision-making, and impaired executive function. Once familiar tasks may become increasingly challenging, leading to frustration and confusion for the person with LBD.
Rem Sleep Behavior Disorder
In individuals with Lewy Body Dementia, REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) is a common advanced symptom. During REM sleep, the stage associated with dreaming, the muscles are usually relaxed to prevent physical movements. However, in RBD, this muscle paralysis is absent, causing individuals to physically act out their dreams.
These actions may range from mild movements like talking or laughing to more substantial and potentially dangerous behaviors such as kicking, thrashing, or even jumping out of bed. This can pose a risk to both the person with LBD and their bed partner, leading to potential injuries and sleep disturbances.
Autonomic Dysfunction
Autonomic dysfunction refers to the disruption of the autonomic nervous system, which controls vital bodily functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, digestion, and body temperature regulation. People with advanced Lewy Body Dementia often experience autonomic dysfunction, which can manifest in various ways.
It is not uncommon for individuals with LBD to experience orthostatic hypotension, a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing. This can result in dizziness, lightheadedness, and an increased risk of falls. Furthermore, autonomic dysfunction can contribute to urinary incontinence, constipation, and difficulty regulating body temperature.
In conclusion, as Lewy Body Dementia progresses, the advanced symptoms it presents can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Recognizing the fluctuations in cognition, the occurrence of REM sleep behavior disorder, and the presence of autonomic dysfunction is crucial for caregivers and healthcare professionals to provide targeted support and manage these symptoms effectively.
Non-cognitive Symptoms
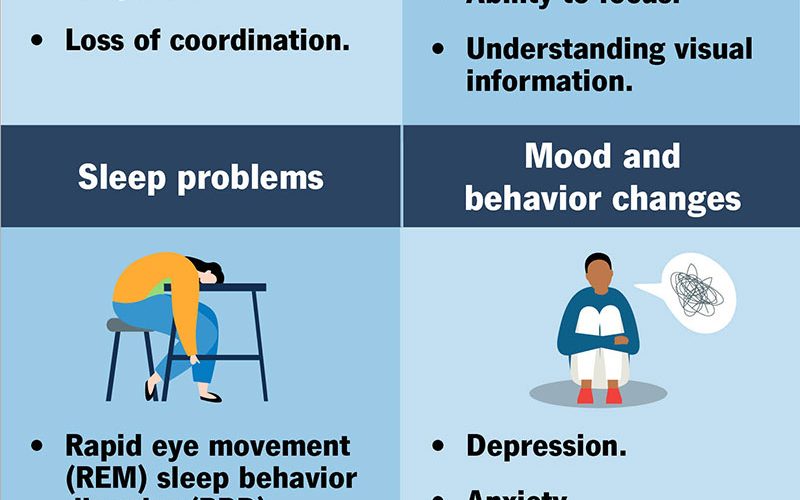
Lewy body dementia is a complex neurodegenerative condition that is characterized by a range of cognitive and non-cognitive symptoms. While cognitive symptoms such as memory loss and confusion are well-documented, non-cognitive symptoms can also have a profound impact on individuals with Lewy body dementia. These non-cognitive symptoms can include behavioral and mood changes, as well as sleep disturbances, which can significantly affect the quality of life for both the individual with dementia and their caregivers.
Behavioral And Mood Changes
Individuals with Lewy body dementia may experience significant changes in their behavior and mood. This can manifest as agitation, anxiety, depression, or sudden fluctuations in mood. Additionally, individuals may exhibit impulsive behavior, aggression, and irritability. These changes can be challenging for caregivers to manage and may contribute to increased stress within the caregiving environment.
Sleep Disturbances
Sleep disturbances are also common in individuals with Lewy body dementia. These disturbances may include difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings throughout the night, and increased daytime sleepiness. Additionally, individuals may experience vivid dreams or hallucinations during sleep, which can be disorienting and distressing. These sleep disturbances can further contribute to worsening cognitive and behavioral symptoms, creating a cycle of challenges for both individuals and their caregivers.
Diagnosing Lewy Body Dementia
Identifying and diagnosing Lewy Body Dementia can be challenging due to its overlapping symptoms with other neurodegenerative conditions. However, a combination of clinical examination, brain imaging, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis can help in making an accurate diagnosis.
Clinical History And Examination:
A thorough clinical history and examination are crucial in diagnosing Lewy Body Dementia. The healthcare professional will evaluate the patient’s cognitive abilities, motor functions, sleep patterns, and psychiatric symptoms. They may also inquire about the timeline and progression of the symptoms.
During the examination, the healthcare professional will observe any parkinsonism features, such as tremors, stiffness, or impaired balance. Additionally, they will look for cognitive impairments, visuospatial difficulties, fluctuating attention, and hallucinations. These symptoms, in conjunction with the clinical history, can provide vital clues for a Lewy Body Dementia diagnosis.
Brain Imaging:
Brain imaging plays a crucial role in supporting the diagnosis of Lewy Body Dementia. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Computed Tomography (CT) scans can help identify any structural abnormalities in the brain. These imaging techniques can detect atrophy or shrinkage in specific areas, such as the hippocampus and neocortex.
In addition to structural imaging, functional imaging techniques like Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) or Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans can assess neuronal activity and identify reduced blood flow or metabolism in regions affected by Lewy Body Dementia.
Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis:
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis is a valuable tool in diagnosing Lewy Body Dementia. By collecting a sample of CSF, healthcare professionals can analyze biomarkers related to the disease. Increased levels of α-synuclein, a protein associated with Lewy bodies, can indicate the presence of Lewy Body Dementia. Additionally, reduced levels of amyloid-beta and tau proteins, commonly found in Alzheimer’s disease, can differentiate Lewy Body Dementia from other neurodegenerative disorders.
It is important to note that these diagnostic tests should be interpreted in conjunction with the patient’s clinical presentation and symptoms. A comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional specializing in neurodegenerative diseases is essential for an accurate diagnosis.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/lewy-body-dementia-stages-progression-98735-01-2050d2180cf54e749c8bb8808352b326.png)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Lewy Body Dementia Symptoms
What Is Life Expectancy For Lewy Body Dementia?
Life expectancy for Lewy body dementia varies depending on various factors. On average, people with this condition live for about six to twelve years from the time of diagnosis. However, some individuals may live longer or shorter depending on their overall health and the progression of the disease.
What Are The First Signs Of Lewy Body Dementia?
The first signs of Lewy body dementia may include visual hallucinations, movement problems, and fluctuations in alertness and attention. Other symptoms may include memory loss and executive function difficulties. It’s important to seek medical advice if these signs are noticed.
What Are The Three Core Features Of Lewy Body Dementia?
Lewy body dementia has three core features: cognitive problems like memory loss, visual hallucinations, and movement difficulties, including tremors.
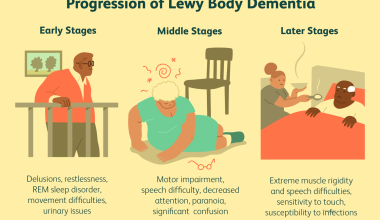
What Are The 7 Stages Of Lewy Body Dementia?
The 7 stages of Lewy body dementia include early stages with subtle cognitive changes, followed by increased difficulty with memory and concentration, heightened visual hallucinations and sleep disturbances, motor symptoms such as slow movements and balance issues, severe cognitive decline with confusion and disorientation, dependence on others for daily activities, and finally, end-stage with limited mobility and increased vulnerability to infections.
Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms of Lewy body dementia is crucial for early detection and management. Recognizing the signs such as visual hallucinations, fluctuating alertness, and Parkinson’s-like motor symptoms can lead to proper diagnosis and treatment. By being aware of these symptoms, individuals and caregivers can better navigate the challenges of this complex condition.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases